Selecting high pressure solenoid valves can be daunting. These valves play a vital role in various industrial applications. Data from the Valve Manufacturers Association indicates that the market for solenoid valves is expected to grow significantly, reaching $3.5 billion by 2025. This growth is driven by demand across sectors like oil and gas, water treatment, and manufacturing.
When choosing high pressure solenoid valves, several factors must be considered. Pressure ratings, materials, and the specific fluid types are crucial. Inadequate selection can lead to performance failures, safety hazards, or even costly downtime. Surprisingly, many users overlook these details. They may focus solely on price, which could lead to dire consequences.
Industry professionals emphasize the importance of matching the valve specifications to operational requirements. However, there is often a disconnect in understanding fluid dynamics. The right choice can enhance efficiency and extend equipment lifespan, but the wrong one can cause disruptions. It’s essential to take the time needed for this decision, ensuring all factors are meticulously evaluated before purchase.

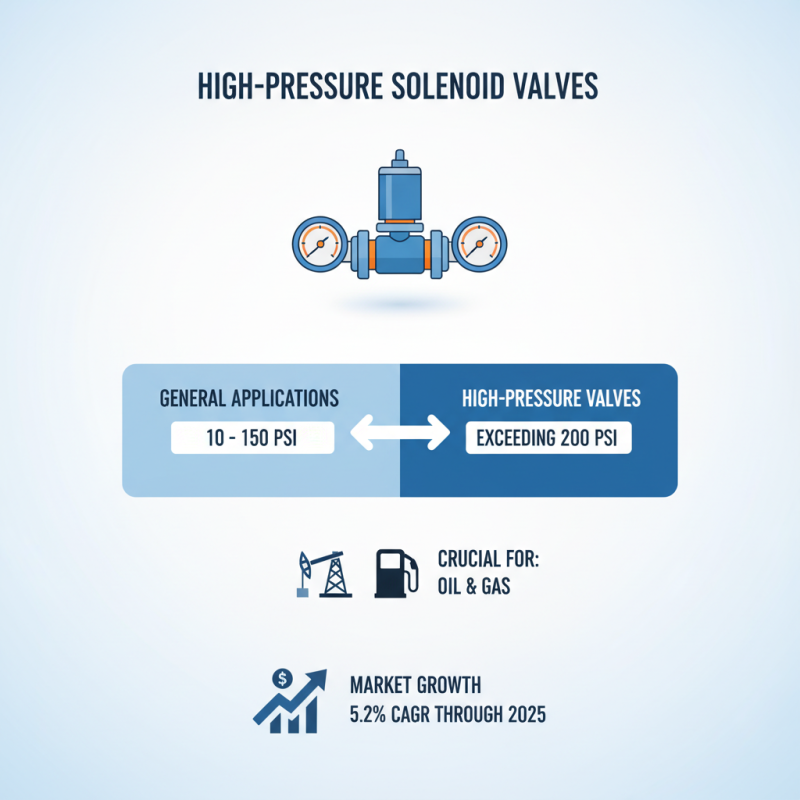
When selecting high-pressure solenoid valves, understanding the operating pressure range is crucial. Solenoid valves typically operate between 10 to 150 psi for general applications. However, high-pressure valves can go beyond 200 psi. This is essential for industries such as oil and gas. Reports suggest that the market for these valves is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate of 5.2% through 2025.
Pay attention to pressure ratings. A valve rated for 300 psi won't perform well if exposed to pressures exceeding that limit. Consider the fluid's characteristics as well. Corrosive fluids may require special materials. Some suppliers recommend stainless steel for enhanced durability.
Tips: Always verify the specifications from multiple sources. Check for any pressure drop issues that might arise. Collaboration with engineering teams can help in making informed choices. High pressures can lead to valve failure if not properly managed. Regular maintenance is essential for safe operations.
Choosing the right material for high-pressure solenoid valves is crucial. The material must be durable and able to withstand harsh conditions.
For instance, stainless steel offers excellent strength. However, it may not be suitable for all fluids.
Compatibility with the fluids is equally important. Some materials corrode faster when in contact with certain chemicals.
For example, brass is commonly used but can react negatively with strong acids. Additionally, plastics may work well for certain applications but might lack the durability needed for high pressure.
It's essential to test and review material performance under specific conditions. Sometimes, manufacturers provide guidelines, but these might not cover all scenarios. Users often encounter issues when the selected material fails. Rethinking material choices can lead to better outcomes. Don't overlook fluid compatibility; it can save time and money.
When selecting high-pressure solenoid valves, flow rate requirements play a crucial role in ensuring optimal performance. A recent industry report highlights that flow rate affects overall system efficiency by up to 30%. This means that a mismatch between the valve capacity and the system's demand can lead to operational issues. For instance, a valve with insufficient flow capacity may cause pressure drops, resulting in sluggish operation or even system failures.
It's essential to calculate the required flow rate accurately. Different applications have unique demands. For example, hydraulic systems may require a higher flow rate than pneumatic systems. Sometimes, users underestimate these requirements. Some systems may operate at just 60% of their potential due to miscalculations. Regular testing and reevaluation of flow rates can mitigate such issues and improve performance.
Understanding the relationship between flow rate and pressure drop is pivotal. Experts suggest that a pressure drop exceeding 10% of the system’s total pressure can compromise efficiency. Additionally, considering temperature variations is vital as it affects viscosity and, consequently, flow rates. A valve’s specifications should be revisited periodically to adapt to changing operating conditions. This iterative approach ensures that the system remains reliable and efficient over time.
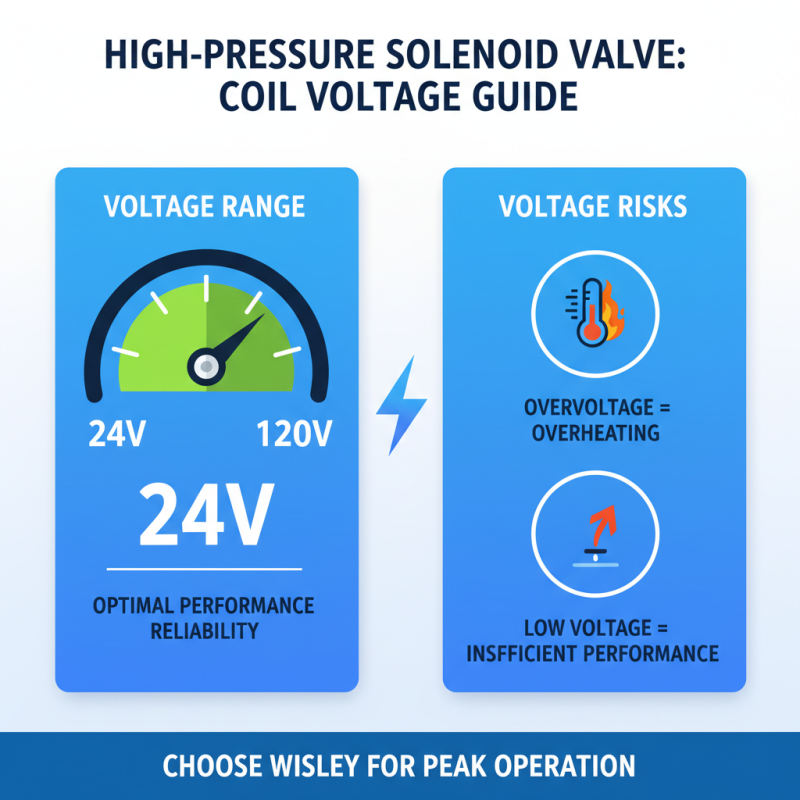
When selecting high pressure solenoid valves, coil voltage and frequency specifications are crucial. The coil voltage directly affects the valve's performance and reliability. Industry reports show that valves operating within a typical range of 24V to 120V tend to perform best in varied applications. However, choosing the right voltage isn’t always straightforward. Over-voltage can lead to overheating, while low voltage might result in insufficient performance.
The frequency at which a solenoid operates also impacts its efficiency. Most solenoid valves function well between 50Hz and 60Hz, but variations exist. In some applications, higher frequencies can enable quicker response times, enhancing overall efficiency. Yet, not all systems are designed for these variations.
Many manufacturers face challenges in matching frequency specifications to their systems. Misalignments can lead to operational inefficiencies. Reports indicate that about 30% of solenoid valve failures stem from incorrect voltage and frequency selections. This emphasizes the need for thorough research on application needs before making a purchase. Finding the right balance is often a process of trial and error. It’s essential to continuously evaluate performance and make necessary adjustments.
When it comes to high-pressure applications, response time is crucial. A fast response time means better control over the system. Delays can lead to inefficiencies or even failures. For example, in an automated assembly line, slow actuators can stall production. This can be costly.
Tips: Always measure the response time of a solenoid valve before making a decision. Consider the entire system's requirements, not just the valve itself.
In some cases, you might find that a valve with a slightly longer response time works better for your specific setup. It’s about finding the right balance. Additionally, consider how temperature and pressure fluctuations will affect response times. Often overlooked, these factors can change performance dramatically.
Tips: Test multiple valves under actual operating conditions. Document their performance. This provides crucial insights for your application.
| Parameter | Description | Value/Example |
|---|---|---|
| Max Operating Pressure | The maximum pressure the valve can handle without failure | 1000 PSI |
| Response Time | Time taken to open or close the valve after activation | 10 ms |
| Body Material | Material used for the valve body, affecting durability and compatibility | Brass |
| Coil Voltage | Voltage required to activate the solenoid | 24 VDC |
| Flow Rate | The amount of fluid that can pass through the valve per unit time | 0.5 GPM |
| Temperature Range | Operating temperature limits for the valve | -10 to 80 °C |



1272 Speers Rd Unit 4
Oakville ON Canada L6L 2X4
©Copyright 2020 Gosco Valves. All rights reserved.