Selecting the appropriate high pressure solenoid valves for your specific applications is critical for ensuring operational efficiency and safety in various industries. According to a recent report by MarketsandMarkets, the high pressure solenoid valves market is anticipated to grow to $2.3 billion by 2025, driven by increased demand for automation and improved system performance. As industries evolve and the need for precision and reliability escalates, understanding the features and specifications of high pressure solenoid valves becomes paramount.
Industry expert Dr. Richard Thompson, a leading authority in fluid dynamics and valve technology, emphasizes the importance of meticulous selection. He stated, "Choosing the right high pressure solenoid valve can significantly influence overall system efficacy and longevity." This assertion highlights that selecting an ill-suited valve can lead to catastrophic failures, operational downtime, and increased costs. As such, it is essential for engineers and procurement professionals to consider various factors, including pressure ratings, material compatibility, and response time, when determining the best high pressure solenoid valves for their needs. This informed approach not only enhances operational performance but also contributes to long-term reliability and maintenance savings.

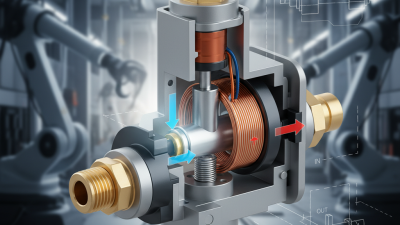
High pressure solenoid valves play a crucial role in various industries where the control of fluid flow is essential. These valves are designed to operate efficiently under high pressure conditions, making them ideal for applications in hydraulic systems, gas pipelines, and steam control systems. Understanding the specific requirements of your application is key to selecting the right solenoid valve. Factors such as fluid type, pressure rating, temperature range, and the required flow rate must all be considered to ensure optimal performance and longevity.
Tips: When choosing high pressure solenoid valves, it is essential to assess the compatibility of the materials used in the valve body and seals with the fluids being handled. Materials such as stainless steel or brass are often preferred for their durability and resistance to corrosion. Additionally, employing valves with a high cycle rate can improve efficiency, especially in processes that require rapid operation.
Another important consideration is the valve's actuation method. Solenoid valves can be either normally closed or normally open, depending on the desired flow control in your system. Understanding the flow direction and system design can help you make the best choice. Furthermore, ensure that the valve's electrical specifications match your control system to guarantee effective integration into your application.
| Application | Pressure Rating (psi) | Valve Type | Material | Operating Temperature (°F) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | 3000 | Direct Acting | Stainless Steel | -40 to 250 |
| Water Treatment | 1500 | Pilot Operated | Brass | 32 to 180 |
| Chemical Processing | 5000 | Normally Closed | PTFE | -20 to 200 |
| HVAC Systems | 2000 | Two-Way | Aluminum | -10 to 140 |
| Food & Beverage | 1500 | Normally Open | Hygienic Stainless Steel | 32 to 180 |

When selecting high-pressure solenoid valves for your specific applications, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. One of the primary considerations is the valve's pressure rating. According to a report from the International Society for Automation (ISA), solenoid valves operating under higher pressure conditions, typically above 150 psi, require robust construction materials to withstand the stress without compromising safety or functionality. Materials such as stainless steel or specialized polymers can enhance durability and reduce the risk of failures in demanding environments.
Another important factor is the valve's flow characteristics, which are crucial for maintaining system efficiency. The flow coefficient (Cv) is a vital parameter that indicates the valve's ability to pass fluid. High-performance solenoid valves typically exhibit a Cv value that aligns with the application's demands. A study by the Fluid Power Institute highlights that improper Cv selection can lead to significant energy losses and reduced system efficiency, emphasizing the need for careful calculations and compatibility checks with the existing system dynamics.
Lastly, it is essential to consider the operating environment, including temperature ranges and potential exposure to corrosive substances. The same ISA report notes that high-pressure solenoid valves should have a temperature tolerance that aligns with the process conditions to prevent failure. Furthermore, factors like electrical requirements, such as voltage and current ratings, must also be evaluated to ensure that the solenoid valves operate correctly within the system's electrical framework, thereby enhancing overall reliability and performance.
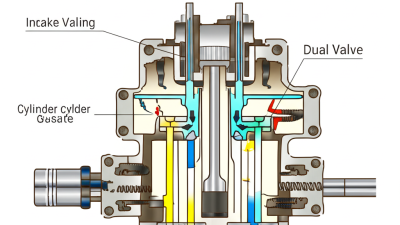
When it comes to selecting high pressure solenoid valves, understanding the different types available is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in your specific applications. The two primary categories are normally closed (NC) and normally open (NO) solenoid valves. Normally closed valves remain shut when de-energized, allowing for controlled flow only when activated, making them ideal for safety applications where fluid leakage must be minimized. In contrast, normally open valves permit flow until an electric current is applied, offering advantages for processes requiring consistent flow and quick shut-off capabilities.
Another significant factor to consider is the valve construction and materials used, particularly when working with high pressure environments. Valves can be made from brass, stainless steel, or plastic, each offering varying levels of durability and corrosion resistance suited for different media. Additionally, the valve's sealing mechanism, such as soft or metal seals, influences its ability to cope with high pressure and temperature extremes. Evaluating these characteristics ensures that you select a valve that not only meets the pressure requirements but also aligns with the operational conditions of your application.
When selecting high pressure solenoid valves, one of the foremost considerations is the compatibility of materials with the fluids involved in your system. Different fluids can greatly affect the longevity and performance of the valve components, often leading to premature failure if the materials are not suited for the application. Conducting a thorough assessment of the chemical properties of the fluid, including its pH level, viscosity, temperature, and potential for corrosion, is crucial. For instance, a valve made from stainless steel may be suitable for water and oil applications but could corrode when exposed to aggressive chemicals like acids or chlorides.
Additionally, environmental conditions can impact material choice. Factors such as temperature extremes, exposure to UV rays, and humidity levels can degrade certain materials over time. For applications involving high temperatures or fluctuating conditions, materials like PTFE or other high-performance polymers may offer better resistance to these elements, prolonging the operational life of the solenoid valve. It is essential to ensure that the selected materials not only withstand the specific fluids but also the environmental conditions they will face to maintain optimal system performance and reliability.
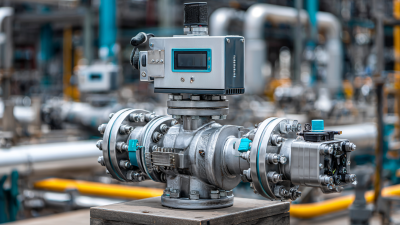
When it comes to installing high-pressure solenoid valves, ensuring optimal performance starts with proper placement and configuration. Position the valve close to its power source to minimize the length of wiring, which can prevent voltage drop and ensure efficient operation. Additionally, ensure that the valve is oriented correctly—if it's a direct-acting solenoid valve, it should be installed in a vertical position. This reduces the risk of debris accumulation that could impair functionality.
Regular maintenance is crucial to keep your solenoid valves functioning effectively. **Tip:** Schedule routine inspections to check for leaks, wear, and electrical connections. Look for any signs of corrosion or damage to the coil and the valve body. Cleaning the valve periodically will also help prevent buildup that can cause malfunctions. **Tip:** Lubricate moving parts as recommended by the manufacturer, but avoid over-lubrication, which could attract dirt and debris.
Lastly, always ensure that the power supply matches the specifications of your solenoid valve. Installing a valve rated for a different voltage can lead to premature failure. **Tip:** Consider implementing a monitoring system that tracks the valve's performance, alerting you to any irregularities early on. By prioritizing installation and maintenance, you can enhance the reliability and longevity of high-pressure solenoid valves in your applications.



1272 Speers Rd Unit 4
Oakville ON Canada L6L 2X4
©Copyright 2020 Gosco Valves. All rights reserved.