In the world of industrial applications, the importance of selecting the right hydraulic solenoid valve cannot be overstated. These crucial components regulate fluid flow, ensuring systems operate efficiently and reliably. However, with various types and specifications available, making the right choice can be a daunting task. As industry expert Dr. Emily Carter, a renowned engineer in hydraulic systems, once stated, "The efficiency and reliability of a hydraulic system hinge on the optimal selection of solenoid valves."
When choosing a hydraulic solenoid valve, several factors must be considered, including the valve's function, operating pressure, and fluid compatibility. Understanding these elements will help engineers and operators avoid common pitfalls that can lead to equipment failure or inefficiencies. A well-chosen hydraulic solenoid valve not only enhances operational performance but also contributes to cost savings in the long run.
Ultimately, proper selection of a hydraulic solenoid valve can significantly enhance the functionality of hydraulic systems across various applications. By following best practices and consulting with experts in the field, users can ensure that they are making informed decisions that will benefit their operational integrity and success.
Hydraulic solenoid valves play a crucial role in the control of hydraulic systems, enabling precise operation of machinery and equipment across various applications. At their core, these valves function by converting electrical energy into mechanical movement. When an electrical signal activates the solenoid, it moves a plunger that opens or closes a port within the valve, thus controlling the flow of hydraulic fluid. This mechanism allows for the automation of processes such as lifting, moving, and applying pressure where needed.
Understanding the different types of hydraulic solenoid valves is essential for selecting the right one for a specific application. Common varieties include normally closed and normally open valves, each serving distinct functions depending on the operational requirements. Additionally, factors such as flow rate, pressure rating, and voltage compatibility must be considered to ensure optimal performance. By comprehensively assessing these elements, operators can select a hydraulic solenoid valve that not only meets their immediate needs but also enhances the overall efficiency and reliability of their hydraulic systems.
| Valve Type | Port Size | Voltage | Flow Rate | Material | Operating Pressure | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Way Normally Closed | 1/4 inch | 12 VDC | 10 GPM | Aluminum | 3000 PSI | Automotive |
| 3-Way Diverter | 3/8 inch | 24 VDC | 15 GPM | Stainless Steel | 2500 PSI | Industrial Machinery |
| 4-Way Double Acting | 1/2 inch | 110 VAC | 20 GPM | Brass | 4000 PSI | Construction Equipment |
| 2-Way Normally Open | 3/4 inch | 24 VDC | 25 GPM | Plastic | 2000 PSI | Agriculture Equipment |
When selecting a hydraulic solenoid valve for your application, several key factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and reliability. One of the foremost considerations is the valve's operating pressure and flow rate, which should match the requirements of your hydraulic system. According to a report by the International Fluid Power Society, approximately 30% of hydraulic system failures can be attributed to improper valve selection regarding these critical specifications. Therefore, accurately assessing the operational demands and consulting fluid power standards can help in making the right choice.
Another important factor is the duty cycle of the solenoid valve. This refers to how long the valve can be energized without overheating. According to a study published by the National Fluid Power Association, the longevity of solenoid valves can vary significantly based on their duty cycle ratings. Selecting a valve with a suitable duty cycle ensures that it can handle the operational demands without risking damage or failure. Additionally, it’s advisable to consider the environmental conditions in which the valve will operate, including temperature extremes and exposure to contaminants, as these can significantly impact functionality and lifespan. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring compatibility and performance in your hydraulic applications.
This bar chart displays the importance of various criteria when selecting a hydraulic solenoid valve for specific applications. Factors such as pressure rating and flow rate are crucial considerations to ensure optimal performance.
When selecting a hydraulic solenoid valve for your system, understanding the different types and their specific applications is crucial. Hydraulic solenoid valves generally fall into three main categories: normally closed, normally open, and proportional valves. Normally closed valves allow fluid flow only when energized, making them ideal for applications requiring fail-safe conditions. Conversely, normally open valves are used in systems where flow is needed by default, cutting off when power is applied. Proportional valves are sophisticated devices that regulate flow and pressure, providing versatility for systems that require precise control.
Tips for selection include evaluating your system’s pressure requirements and flow rates. Ensure the valve can handle the maximum pressure your application demands. Additionally, consider the type of fluid being used, as compatibility can impact the performance and longevity of the valve. It's also important to look at the duty cycle of the solenoid, ensuring it aligns with your operational needs.
Moreover, systematic integration is key. Look for valves that align well with your hydraulic circuit design. Remember that proper installation and maintenance can greatly extend the service life of your valve. Consulting with hydraulic system professionals can also provide insights tailored to your specific applications, leading to informed decisions.
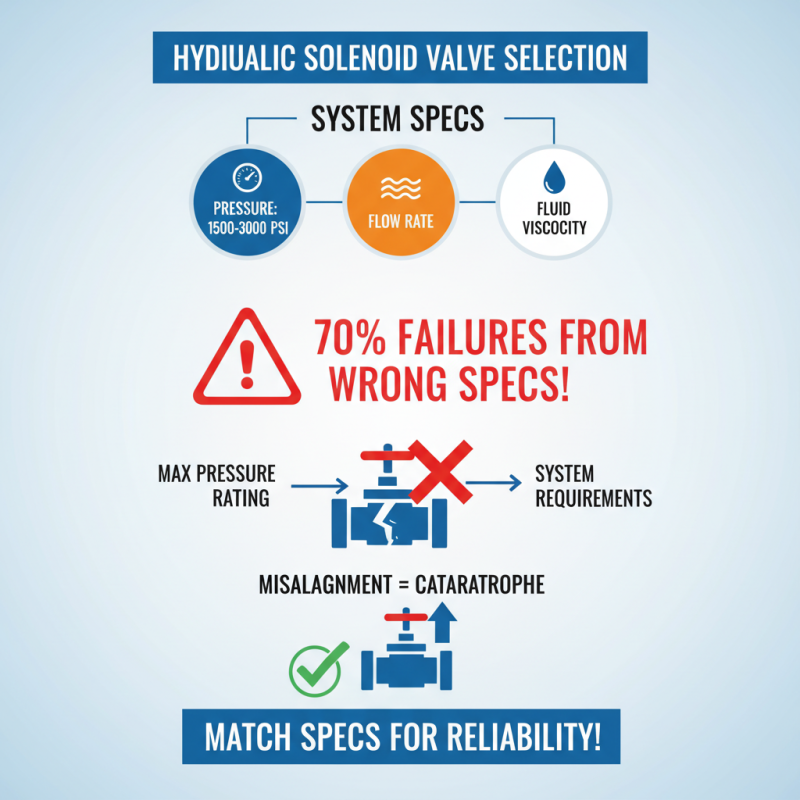
When selecting a hydraulic solenoid valve, one of the critical steps is determining the specifications of your hydraulic system. This involves analyzing factors like pressure, flow rate, and fluid viscosity. According to a report by the International Fluid Power Society, approximately 70% of hydraulic system failures are attributed to improper specification and selection of components. Hence, understanding the required pressure range is vital; most hydraulic systems operate between 1,500 to 3,000 psi. Failure to align your solenoid valve's maximum pressure rating with system requirements can lead to catastrophic failures.
In addition to pressure considerations, flow rate is essential for optimal performance. A study published in the Journal of Hydraulic Engineering indicates that effectively sizing a valve entails assessing the system’s flow rate, which can vary widely from one application to another—common values can range from 5 to over 500 gallons per minute (GPM). Furthermore, the viscosity of the hydraulic fluid must be factored in as it affects flow characteristics and valve responsiveness. Manufacturers often provide flow coefficient (Cv) values for solenoid valves, offering a guideline for matching the valve to your system's flow demands. By meticulously determining these specifications, users can select hydraulic solenoid valves that enhance performance and durability while minimizing the risk of failure.
When installing hydraulic solenoid valves, adherence to best practices can significantly enhance operational efficiency and longevity. It is crucial to ensure proper alignment during installation, as misalignment can lead to premature wear and failure. According to a report from the International Fluid Power Society, nearly 30% of hydraulic system failures are attributed to installation errors. Additionally, the use of quality seals and fittings is recommended, as poor-quality components can introduce leakage, reducing the effectiveness of the system and increasing maintenance costs.
Regular maintenance of hydraulic solenoid valves is equally vital for their optimal performance. Scheduled inspections should be part of a comprehensive maintenance program, as they can identify potential issues before they escalate. The Institute of Hydraulics Engineering suggests that implementing a routine maintenance schedule can extend the lifespan of hydraulic equipment by up to 50%. Cleaning the valve body and ensuring that electrical connections are secure can also prevent system malfunctions. Utilizing diagnostic tools to monitor valve performance can yield insights into operational conditions, allowing for timely adjustments and minimizing downtime. By following these best practices, users can ensure that their hydraulic systems remain reliable and efficient over time.




1272 Speers Rd Unit 4
Oakville ON Canada L6L 2X4
©Copyright 2020 Gosco Valves. All rights reserved.