In the realm of industrial automation, the importance of precise control of fluid flow cannot be overstated. A pneumatic control valve is a critical component that facilitates this control in various applications, utilizing compressed air to operate mechanisms that manage the flow of gases or liquids. Through its operation, the pneumatic control valve plays an essential role in ensuring that production processes run smoothly and efficiently, thereby enhancing operational productivity.
Understanding how a pneumatic control valve works involves delving into its design and functionality. These valves can be adjusted to varying positions, allowing for accurate modulation of flow rates and pressure levels in a system. By employing pneumatic pressure, these valves respond swiftly to changing operational conditions, making them ideal for dynamic industrial environments. The versatility of pneumatic control valves enables their application across numerous sectors, including manufacturing, chemical processing, and waste management, highlighting their significance in modern industrial practices.
As we explore the specific mechanisms and advantages of pneumatic control valves, we will uncover their vital contributions to maintaining reliable and efficient system operations. This understanding not only elucidates their role but also emphasizes the impact of pneumatic technologies on the continuous advancement of industrial applications.
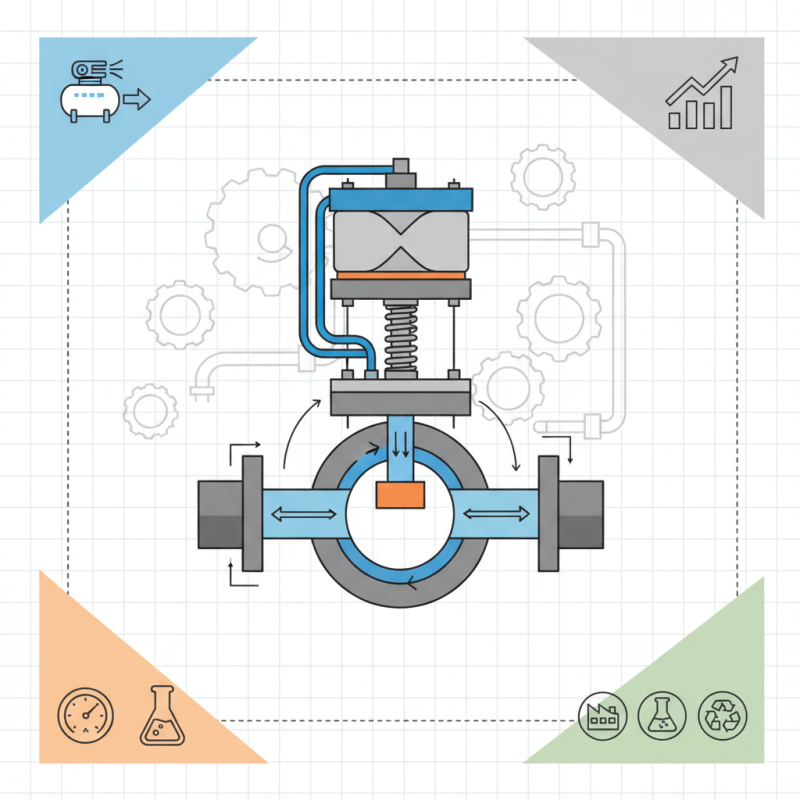
A pneumatic control valve is a critical component used in various industrial applications to manage the flow of air or gas. Essentially, it acts as a gatekeeper, controlling the passage of the fluid based on external commands. These valves are designed to function using compressed air, which operates a diaphragm or piston mechanism inside the valve. When the compressed air is introduced, it moves the internal components, allowing the valve to open, close, or modulate flow as needed.
In industrial settings, pneumatic control valves are often employed in automation systems. They play a crucial role in regulating processes such as pressure control, temperature management, and fluid movement in manufacturing lines. The responsiveness and reliability of these valves make them an ideal choice for environments that require quick adjustments and precise control. As such, they contribute significantly to enhancing efficiency and safety in various industrial operations.
Pneumatic control valves are essential components in various industrial applications, facilitating the regulation and control of fluid flow. Understanding the key components of these valves is crucial for optimizing their performance. A pneumatic control valve typically consists of several main parts: the actuator, the valve body, and the positioner. The actuator, usually powered by compressed air, is responsible for moving the valve mechanism to open or close the flow path. According to a report by the Global Valve Market Research Institute, the actuator often accounts for nearly 40% of the valve’s total cost, emphasizing its importance in system efficiency.
The valve body houses the internal components that regulate flow. It can be designed in various configurations, such as globe, ball, or butterfly designs, each suited for specific applications. Additionally, the positioner is another critical component that ensures the valve opens and closes at the correct times, maintaining the desired flow rate. According to a report from the International Society of Automation, properly calibrated positioners can enhance an industrial system’s efficiency by up to 20%. Alongside these mechanical components, sensors play a crucial role in providing real-time feedback, enabling precise control based on operational demands. As industries increasingly adopt automation, the integration of advanced pneumatic control valves is essential for achieving better process control and energy efficiency across the board.
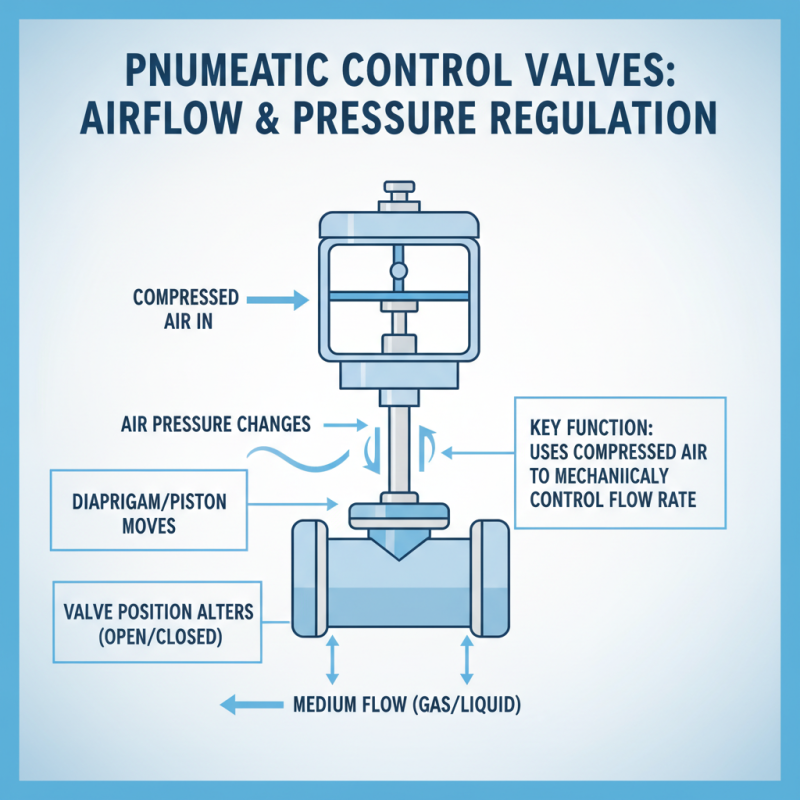
Pneumatic control valves are essential components in various industrial applications, enabling precise control of airflow and pressure within systems. These valves operate mechanically by utilizing compressed air to control the opening and closing of the valve. Typically, a diaphragm or piston in the valve responds to changes in air pressure, allowing it to regulate the flow of gases or liquids. As the pressure varies, the diaphragm moves, changing the valve’s position between fully open and fully closed, thus controlling the medium's flow rate.
Tips: To ensure optimal performance of pneumatic control valves, it's important to regularly inspect and maintain the components, as wear and tear can affect their efficiency. Check for leaks in the pneumatic lines, and ensure that the air supply is clean and free from moisture, which can cause corrosion and operational issues.
In addition to mechanical operation, the design of pneumatic control valves often includes features like failsafe positions and manual overrides. This ensures stability in case of a power failure or emergency, allowing for safe operation. Understanding the mechanical workings and proper maintenance of these valves is crucial for engineers and technicians working in environments where precise fluid control is critical.
Pneumatic control valves play a crucial role across various industrial applications by regulating the flow of gases or air through pressurized systems. These valves are commonly found in sectors such as manufacturing, oil and gas, and food processing, where precise control over fluid movement is essential.
 According to a recent market analysis by Research and Markets, the global pneumatic valve market was valued at approximately $4.1 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $6.1 billion by 2028, indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for automation in industrial processes, as pneumatic control valves contribute to enhanced efficiency and safety.
According to a recent market analysis by Research and Markets, the global pneumatic valve market was valued at approximately $4.1 billion in 2021 and is projected to reach $6.1 billion by 2028, indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.8%. This growth is driven by the increasing demand for automation in industrial processes, as pneumatic control valves contribute to enhanced efficiency and safety.
In manufacturing, pneumatic control valves facilitate the automation of assembly lines, ensuring consistent pressure and flow rates that are vital for the operation of machinery. In the oil and gas sector, these valves help manage the extraction and transportation of natural resources. A report by Grand View Research highlights that the demand for pneumatic valves in this sector is fueled by the need for reliable operation in harsh environments. Additionally, in the food processing industry, pneumatic control valves are employed to maintain hygiene standards while controlling the movement of liquid ingredients, ensuring that production meets both efficiency and regulatory requirements. The versatility and reliability of pneumatic control valves continue to make them indispensable in modern industrial applications.
Pneumatic control valves play a crucial role in automation systems across various industrial applications by regulating the flow and pressure of pneumatic systems. The benefit of using pneumatic control valves lies in their responsiveness and efficiency, which significantly contribute to enhancing operational productivity. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global pneumatic control valves market is projected to reach USD 5.2 billion by 2025, growing at a CAGR of 6.5%, highlighting the increasing adoption of automation technologies that rely heavily on these components.
One of the key advantages of pneumatic control valves is their ability to provide precise control over processes. This precision not only optimizes performance but also reduces the likelihood of system failures, which can lead to costly downtime. A study by the International Society of Automation (ISA) revealed that organizations implementing pneumatic control systems can achieve a reduction of up to 30% in energy consumption while improving throughput. Additionally, pneumatic control valves are often easier to maintain and operate in comparison to their hydraulic or electric counterparts, lowering the total cost of ownership and enhancing flexibility in system design. As industries strive for greater efficiency and smarter solutions, the adoption of pneumatic control valves is set to continue its upward trend.




1272 Speers Rd Unit 4
Oakville ON Canada L6L 2X4
©Copyright 2020 Gosco Valves. All rights reserved.